Partnering Together: To Help You Navigate the Future of Chronic Kidney Disease
For all appropriate patients:Potentially eliminate or reduce the cost of dialysis1 Reduce costs for the capitated population1 Improve care
coordination2 Raise awareness about living kidney donation2 Put your patients with Chronic Kidney Disease on the Path to a Pre-Dialysis TransplantIncreasing access to pre-dialysis transplants may
benefit you and your beneficiaries1,3
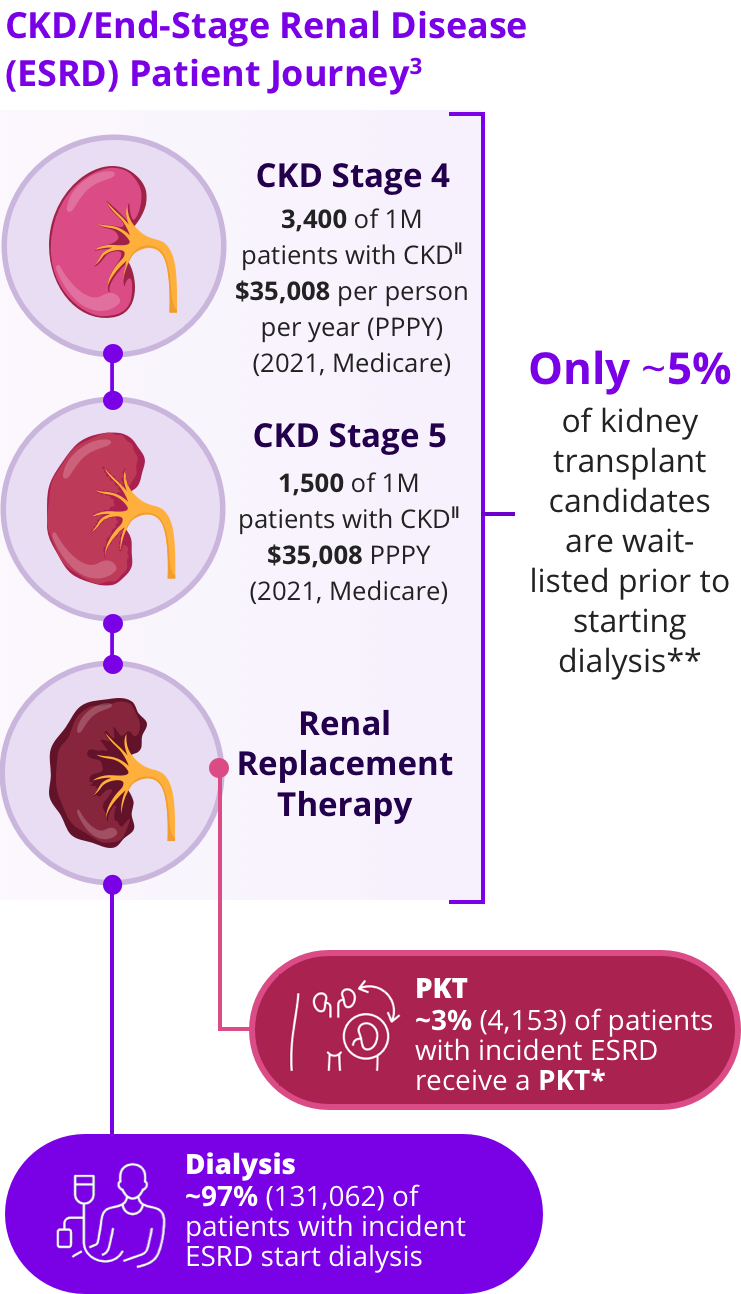
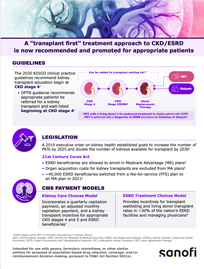
 Kidney Failure
Kidney FailureAnnually there are
~136,000 patients diagnosed with kidney failure3,*
 Dialysis
DialysisMost of these patients will follow a path that leads them to dialysis3,*
 Kidney Transplant
Kidney TransplantOnly ~3% (4,153) of patients will receive preemptive kidney transplant (PKT), the therapy recommended by Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO)3,4,*
For all appropriate patients:

Potentially Eliminate or Reduce Your Medical Spend for Dialysis1,3

Commercial insurance reimburses for dialysis at a higher rate than Medicare7
PKT offers significant cost savings vs non-PKT with commercial insurance8,¶


Raise Awareness About Living Donation9,10
Identify, educate, and refer transplant eligible patients
Early kidney disease education (KDE) (eg, at chronic kidney disease [CKD] stage 4) can lead to an increased use of living donor PKT9,#

of kidney transplant candidates underwent a living donor kidney transplant with early education9,#

of patients wait-listed before dialysis received a living donor kidney transplant 3 years after the preemptive listing10

Improve Fragmented Care3,10-13
- Identifying and educating patients with CKD earlier can improve care and reduce barriers to transplant.11
- Calculate your patient's Estimated Post Transplant Score (EPTS) to identify recipients who may benefit most from rapid waiting list placement and transplantation.10
Candidates are less likely to lose their top-tier EPTS status when they are preemptively wait-listed.10

From 2015-2017, only 1 in 5 kidney transplant candidates with top-tier EPTS scores were preemptively wait-listed for transplant.10

Candidates with a top 20% EPTS status have preferential access to deceased donor kidney offers with the lowest cumulative risk factors.10

Only 37% of patients with top 20% ETPS status were added to the waiting list within 3 years of dialysis initiation.10
Use of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid (CMS) KDE benefit can help increase your PKT population12
In 2018, only ~1% of eligible patients with CKD stage 4 had a claim for kidney disease education13
Utilization of the CMS KDE benefit resulted in:

increase in pre-ESRD wait-listing12,††

increase in PKT12,††

Improve Health Outcomes3,14
With a living donor (LD), your kidney transplant candidates may achieve:

Stay Up-to-Date with Professional Guidelines
15Educate at CKD stage 3, refer at CKD stage 4, and transplant at CKD stage 515,¶¶
Educate at CKD stage 3, refer at CKD stage 4, and transplant at CKD stage 515,¶¶

The Advancing American Kidney Health (AAKH) Initiative aims to double the number of kidneys available for transplant by 2030, through strategies such as increasing available options for individuals in need of kidney transplants and access to PKT.2
Resources to Support Your Appropriate Patients on the Journey to LD PKT
Bring the experts in kidney transplant education to your patients! Click on each resource to learn more.
EXPLORE Transplant: Meet with EXPLORE Transplant, an evidence-based education platform to coach patients and potential donors through the transplant decision process. Patients can also record their own stories to create awareness and address the living donor shortage.
Rejuvenate: Meet with Rejuvenate Kidney Transplant Solutions, which offers a full range of transplant solutions to increase earlier access to care, locate donors, and reduce health care spend.
EPTS Calculator: Calculate your patient’s EPTS score to identify candidates with the longest expected posttransplant survival.

Share
AAKH, Advancing American Kidney Health; AST, American Society of Transplantation; CKD, chronic kidney disease; CMS, Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services; DD, deceased donor; EPTS, estimated post transplant score; ESRD, end-stage renal disease; KDE, kidney disease education; KDIGO, Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes; LD, living donor; OPTN, Organ Procurement Transplant Network; PKT, preemptive kidney transplant; PPPY, per person per year; RRT, renal replacement therapy; USRDS, United States Renal Data System.
*
Incident cases of ESRD in 2021, USRDS.3
†
Inflation-adjusted PPPY 2021.3
‡
Included medical claims of 12,392 patients from 2012 to 2019.5
§
Included 18,453 cases (9,962 kidney, 4,831 liver, 1,638 heart, 1,468 lung, and 554 pancreas) with case effective dates between January 1, 2010, and April 30, 2014, and claims paid through September 30, 2014.6
¶
Based on a study that identified recipients of first kidney transplants from 2008 to 2015 utilizing the OptumLabs Data Warehouse, which included administrative claims data on privately insured and Medicare Advantage enrollees in the United States. Of 1,544 kidney transplant recipients (1,313 [85%] commercially insured), 725 (47%) received a PKT (565 LD + 160 deceased donor [DD]) and 819 (54%) received a non-PKT (464 LD + 355 DD).8
#
A group education session covering renal replacement therapy options (RRT) was conducted in adults aged >18 years with ESRD (n=80) in the Netherlands (2011-2013); RRT outcomes (date and type) up to 2 years post intervention were collected.9
‖
Based on prevalence of CKD in 2021.3
**
Incident cases of ESRD in 2021, United States Renal Data System (USRDS) ESRD and OPTN waiting list history.3
††
Based on 2013-2017 US data from adults aged ≥67 years who had CKD stage 4 (n=106,465); use of kidney disease education was examined in the 2 years prior to ESRD onset.12
‡‡
Among PKT recipients.14
§§
Based on survival probability of living donor transplant vs hemodialysis reported for 2017.3
¶¶
CKD stage 3, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) 30-59 mL/min/1.73 m2; CKD stage 4, eGFR 15-29 mL/min/1.73 m2; CKD stage 5, eGFR <15 mL/min/1.73 m2 or on dialysis.15
References: 1. Optum. Kidney Solutions: Preemptive Transplants Rates and Cost Savings. Eden Prairie, MN; Optum Inc; August 2021. 2. US Department of Health and Human Services. Advancing American kidney health. https://aspe.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/private/pdf/262046/AdvancingAmericanKidneyHealth.pdf. Accessed January 27, 2024. 3. United States Renal Data System. 2023 USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2023. 4. Chadban SJ, et al. Transplantation. 2020;104(4S1 Suppl 1):S11-S103. 5. League RJ, et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(10):e2239131. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.39131. 6. Irwin FD, et al. Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2016;30(2):71-76. 7. Childers CP, et al. JAMA Intern Med. 2019;179(8):1136-1138. 8. Dean P, et al. Am J Transplant. 2018;18(suppl 4):467. ATC abstract 577. 9. Massey EK, et al. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016;31(5):823-830. 10. Schold JD, et al. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021;32(7):1733-1746. 11. Helmick RA, et al. Transplant Direct. 2018;4(4):e356. doi:10.1097/TXD.0000000000000773. 12. Johansen KL, et al. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020;31(suppl):18. Kidney Week abstract FR-OR11. 13. United States Renal Data System. 2020 USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2020. 14. Huang Y, et al. Nephrol Ther. 2012;8(6):428-432. 15. Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN). Educational guidance on patient referral to kidney transplantation. https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/professionals/by-topic/guidance/educational-guidance-on-patient-referral-to-kidney-transplantation/. Accessed December 11, 2023.
 Sanofi U.S.
Sanofi U.S.
 Dialysis
Dialysis Kidney Transplant
Kidney Transplant












